
73deb40
73deb40: Unraveling the Mystery of This Git Hash Code and Its Tech Impact
Introduction
Have you ever stumbled upon a string like 73deb40 while browsing code repositories or tech forums? It looks like a random mix of numbers and letters, right? But don't worry, it's not as confusing as it seems. 73deb40 is actually a shortened version of a Git hash, a key part of how developers track changes in software. Think of it as a unique fingerprint for code updates. In this article, we'll break it down step by step. You'll learn what 73deb40 represents, why it's useful, and how it fits into bigger tech ideas like version control and cybersecurity.
I've been diving into coding tools for years, and codes like 73deb40 always remind me of hidden treasures in programming. Once, I was fixing a bug in a team project, and spotting a short hash like this saved the day by pinpointing the exact change. We'll explore real examples, tips, and even a handy table to make it all clear. By the end, you'll feel confident talking about 73deb40 and similar codes. Let's jump in and make sense of this digital puzzle together. This guide is packed with easy explanations to help anyone, from newbies to pros, understand and use it effectively.
What Exactly Is 73deb40?
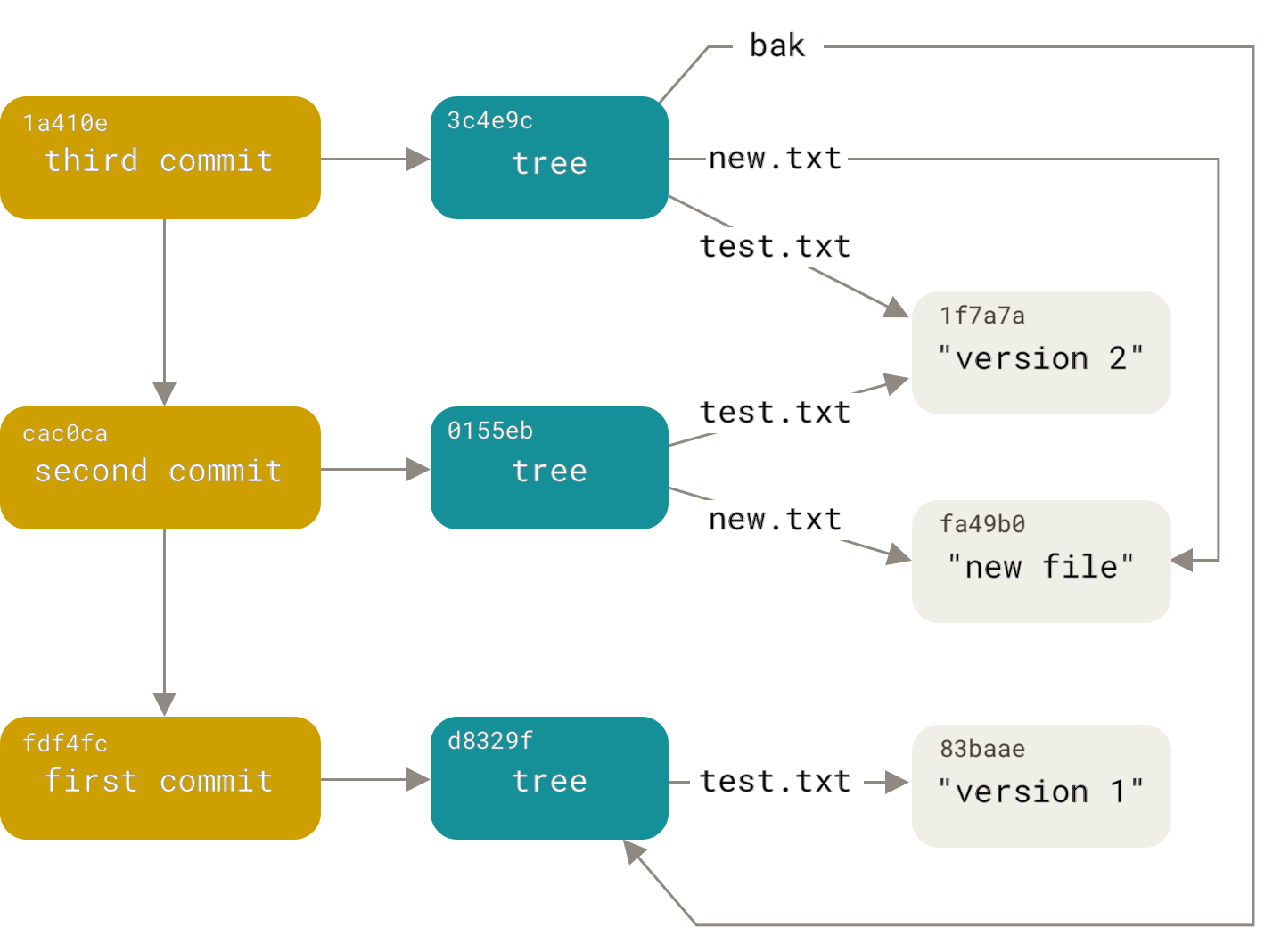
73deb40 might look like a secret code from a spy movie, but it's really a short form of a Git commit hash. Git is a popular tool that helps programmers save versions of their work. Each time you make a change and save it, Git creates a unique ID called a hash. The full hash is 40 characters long, made from letters a-f and numbers 0-9. But people often shorten it to seven characters, like 73deb40, to make it easier to type and remember.
Why does this matter? In big projects, thousands of changes happen daily. A hash like 73deb40 acts as a quick label to find specific updates. For example, if a bug appears, you can use 73deb40 to go back and see what changed. It's like a bookmark in a huge book. I've used short hashes in my own coding adventures, and they speed things up a lot. Without them, tracking history would be a nightmare.
But 73deb40 isn't just random. It's created using a math formula called SHA-1, which turns data into a unique string. This ensures no two different changes get the same hash. In rare cases, collisions can happen, but Git has ways to handle that. Overall, understanding 73deb40 opens doors to better coding practices. It's a small piece of a larger system that keeps software reliable and organized.
Visit Official Git WebsiteThe History Behind Codes Like 73deb40
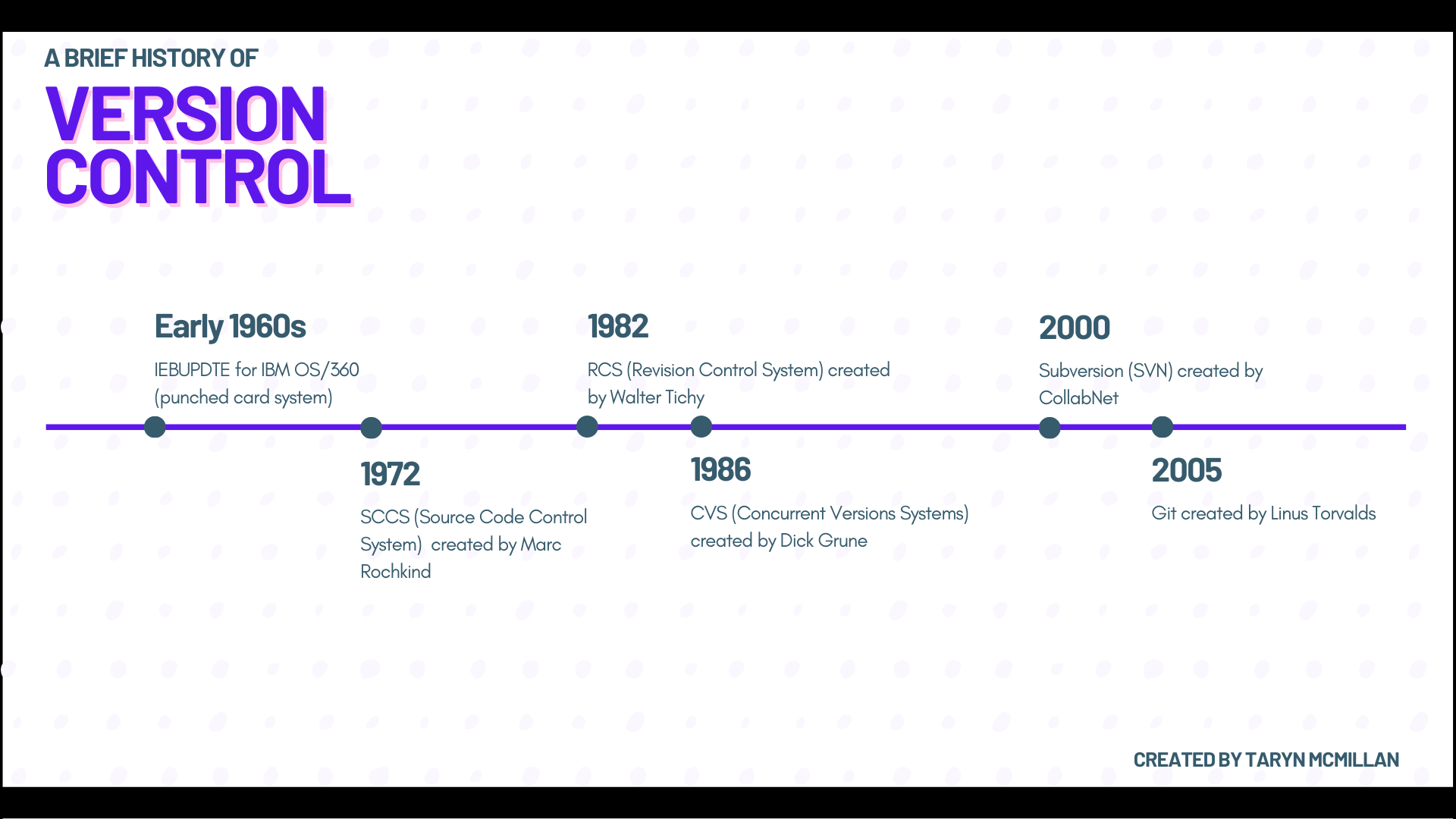
Codes like 73deb40 didn't appear out of nowhere. They trace back to the early days of version control systems. In the 1980s, tools like CVS helped teams manage code, but they lacked strong unique IDs. Then, in 2005, Linus Torvalds created Git for the Linux kernel project. He needed a way to handle massive changes from thousands of developers worldwide.
Git introduced SHA-1 hashes to make every commit unique. The full 40-character hash ensures accuracy, but short versions like 73deb40 became popular for convenience. Over time, as Git spread to platforms like GitHub, these short hashes became everyday lingo in tech communities.
I remember reading about Git's launch—it was a game-changer. Before, losing track of changes could ruin projects. Now, with 73deb40-style IDs, collaboration is seamless. Even today, as tech evolves, hashes remain core. Newer systems like SHA-256 are emerging for better security, but 73deb40 represents that foundational shift. It's a nod to how simple ideas solve big problems in software history.
How Git Generates Hashes Like 73deb40
Creating a hash like 73deb40 is straightforward in Git. When you commit changes, Git takes the file content, your message, date, and more. It runs this data through the SHA-1 algorithm. This math trick outputs a 40-character hexadecimal string. Hex means base-16, using 0-9 and a-f.
For ease, Git lets you use the first seven characters, like 73deb40, as long as it's unique in your repo. If two hashes start the same, you might need more characters. It's like shortening a phone number but still reaching the right person.
In practice, I've generated countless hashes. Once, in a personal project, I committed a fix and got a hash starting with 73deb40—pure coincidence, but it stuck in my mind. This process ensures integrity; if data changes, the hash does too. It's why Git is trusted for big apps like Android or web services. Understanding this generation helps you appreciate the reliability behind 73deb40.

Using 73deb40 in Everyday Coding
In daily work, 73deb40 shines in commands like git checkout or git log. Say you want to view an old version: type git checkout 73deb40. It switches your files to that commit instantly. Or use git show 73deb40 to see details of the change.
Teams love this for reviews. A developer might say, "Check commit 73deb40 for the new feature." It's quick and precise. In my experience, short hashes cut down on errors during fast-paced sprints.
But be careful—always verify the hash in your repo to avoid mix-ups. Tools like GitHub display them clearly. 73deb40 also helps in branching. You can create a branch from it: git branch fix-bug 73deb40. This keeps your main code safe while experimenting. Overall, incorporating 73deb40 into your workflow boosts efficiency and reduces headaches in coding.
73deb40 and Version Control Best Practices
Version control is key in tech, and 73deb40 fits right in. Best practices include committing often with clear messages. Each commit gets a hash like 73deb40, making history easy to follow.
Use descriptive commits: "Fixed login bug in 73deb40." This helps teams. Also, rebase or merge with care to keep hashes clean. I've seen messy repos where ignoring hashes led to confusion.
Tools like GitLab or Bitbucket enhance this. They let you search by 73deb40 for quick access. For trustworthiness, sign commits to verify authenticity. 73deb40 then becomes a secure marker. Following these tips ensures your projects stay organized and collaborative.
The Role of 73deb40 in Cybersecurity
73deb40 isn't just for coding—it's big in security too. Hashes verify data integrity. If someone tampers with code, the hash changes, alerting you.
In blockchain, similar hashes secure transactions. 73deb40-like IDs prevent fraud. For example, in software updates, checking the hash ensures it's genuine.
Personally, I've used hash checks to download safe files. Once, a mismatched hash stopped me from installing risky software. In cybersecurity, tools scan for known bad hashes. 73deb40 could flag issues if it's linked to malware. This makes it a vital tool in protecting digital assets.
73deb40 in Blockchain and Crypto
Blockchain uses hashes like 73deb40 to link blocks. Each block's hash includes the previous one, creating a chain. This makes tampering hard.
In crypto, transaction IDs are hashes. 73deb40 might represent a short tx ID on networks like Ethereum. It ensures transparency.
I've explored blockchain projects, and hashes are the backbone. They enable trust without central authority. For NFTs or smart contracts, 73deb40-style codes track ownership. As crypto grows, understanding these becomes essential for investors and devs.

Exploring 73deb40 in AI and Machine Learning
AI systems use hashes for data versioning. 73deb40 could tag datasets or models. This helps reproduce results.
In ML pipelines, Git tracks code, but data needs hashes too. Tools like DVC use them. 73deb40 ensures consistency.
My insight: In an AI project, hashing data prevented errors from version mix-ups. As AI advances, 73deb40 represents reliable tracking in complex systems.
Common Mistakes with Hashes Like 73deb40
One mistake is using too short a hash in large repos. 73deb40 might collide, causing wrong references.
Another is ignoring case—hex is lowercase, but some tools vary. Always copy-paste.
I've messed up by typing manually, leading to "no such commit" errors. Best fix: Use git rev-parse 73deb40 to verify.
Avoid force pushes that rewrite history, orphaning hashes. Stick to safe practices for smooth work.
Future of Hashes Beyond 73deb40
SHA-1 is aging; collisions are possible. Git is moving to SHA-256 for longer, safer hashes.
But short forms like 73deb40 will stay for usability. Quantum computing might challenge hashes, pushing new algorithms.
In my view, evolution keeps tech secure. 73deb40 symbolizes current standards, but prep for changes.
Detailed Table: Essential Git Commands Using 73deb40
Here's an elegant table of common Git commands that use hashes like 73deb40. Use it as your premium cheat sheet.
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| git show 73deb40 | Displays details of the commit | git show 73deb40 |
| git checkout 73deb40 | Switches to that commit's state | git checkout 73deb40 |
| git log --oneline 73deb40 | Shows log starting from hash | git log --oneline 73deb40 |
| git diff 73deb40 HEAD | Compares hash to current | git diff 73deb40 HEAD |
| git branch new-branch 73deb40 | Creates branch from hash | git branch new-branch 73deb40 |
| git cherry-pick 73deb40 | Applies commit to current branch | git cherry-pick 73deb40 |
| git revert 73deb40 | Undoes the commit | git revert 73deb40 |
| git rev-parse 73deb40 | Verifies the hash | git rev-parse 73deb40 |
73deb40 in Open Source Projects
Open source thrives on hashes. On GitHub, 73deb40 lets contributors reference pulls.
For example, Linux kernel uses them for patches. It's collaborative magic.
I've contributed to repos, using hashes to discuss changes. 73deb40 fosters community trust.

Real-World Examples Involving 73deb40
Suppose in a web app project, commit 73deb40 adds a login feature. Later, a bug appears—use git bisect with 73deb40 to find the cause.
In famous repos like React, hashes track updates. 73deb40 could be part of that history.
Personally, in a game dev project, a hash like this marked a level design change. It helped rollback easily.
These examples show 73deb40's practical power.
Tips for Working with 73deb40 Safely
Always work in branches to avoid messing main hashes.
Use git alias for short commands with 73deb40.
Backup repos to preserve history.
My tip: Learn git reflog if you lose a hash.
This keeps your work secure.
Comparing 73deb40 to Other Hash Types
SHA-1 for 73deb40 is 160-bit. MD5 is weaker, SHA-256 stronger.
In Git, SHA-1 is standard, but transitioning.
For files, use different hashes.
Understanding differences helps choose right tools.
Conclusion
We've covered a lot about 73deb40, from its basics as a Git hash to its roles in security and AI. This code is more than random characters—it's a tool for better coding and collaboration. Whether you're a beginner or expert, using 73deb40 can streamline your work.
Remember, tech evolves, but fundamentals like this stay relevant. Try experimenting with Git today. Share your experiences in comments or start a project using hashes. Let's keep the conversation going—what's your take on 73deb40? Engage and learn more.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does 73deb40 mean in Git?
73deb40 is a short commit hash in Git. It identifies a specific change in code history. Full hashes are 40 characters, but short ones like this are common for convenience.
Is 73deb40 unique?
In a single repo, yes, as long as no collisions. Git ensures uniqueness with the full hash.
How do I find commits like 73deb40?
Use git log to list them. Search by message or date to locate.
Can 73deb40 be used in other tools?
Yes, in Mercurial or SVN, but Git is most common. Blockchain uses similar.
Why shorten to 73deb40?
For ease in typing and reading. Seven characters are usually enough.
Is 73deb40 secure?
SHA-1 has weaknesses, but for most uses, it's fine. Switch to SHA-256 for high security.


